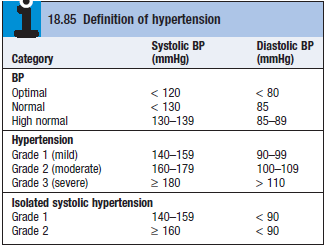
Classification
Etiology
- >95% of cases don’t have an underlying cause – essential HTN
- Multifactorial etiology – e.g. renal dysfunction, peripheral resistance vessel tone, endothelial dysfunction, autonomic tone, insulin resistance
- HTN is MC in African American and Japanese
- Environmental factors – salt intake, alcohol, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, impaired intrauterine growth
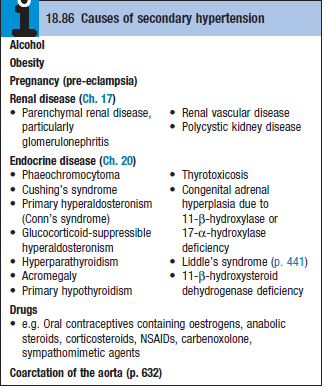
- 5% of cases of HTN are due to a specific cause – secondary HTN (see table)
Pathogenesis
Systolic BP – indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls when the heart beats.
- SBP correlates with SV and the compliance of the aorta
- Determinants of SV are – Preload/afterload and contractility
- Vessel elasticity determines the compliance of the aorta (the ability of the aorta to expand with blood during systole)
- Compliance decreases with age due to ↓elasticity
- ↑SBP is caused by
- ↑preload, ↑contractility, ↓compliance of aorta
- ↓SBP is caused by
- ↓preload, ↓contractility, ↑afterload (e.g. severe aortic stenosis)
Diastolic BP – indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls while the heart is resting between beats.
- DBP correlates with the volume of blood in the aorta during systole
- DBP depends on the tonicity of the smooth muscle cells in the PVR arterioles, the viscosity of blood and the HR
- ↑DBP is caused by
- Vasoconstriction of the PVR arterioles – a greater volume of blood is present in the artery while the heart is filling up in diastole
- Increased blood viscosity – e.g. polycythemia vera
- Increased HR – decreases filling of the ventricles, leaving a greater volume of blood in the aorta during diastole
- ↓DBP is caused by
- Vasodilation of PVR arterioles
- Severe anemia – which decreases blood viscosity
- Decreased HR
Role of sodium in HTN
- Increases plasma volume
- This increases SV, which increases BV
- Causes vasoconstriction of PVR arterioles
- ↑Na in smooth muscle increase Ca-mediated contraction, causing ↑DBP
