- Chronic inflammatory disease characterised by fibrosis and destruction of exocrine pancreatic tissue. DM occurs in advanced cases because islets of Langerhans are involved
Etiology
- Alcohol – stimulates exocrine secretion, causes spasm of Ampulla of Vater
- Hyperparathyroidism – hypercalcemia, stimulates exocrine secretion
- Predisposes to precipitation of protein aggregates within the main pancreatic ductal system
- Congenital anomalies of pancreatic duct – pancreatic divisium
- Pancreatic trauma
- Developing countries – tropical pancreatitis due to nutritional deficiencies
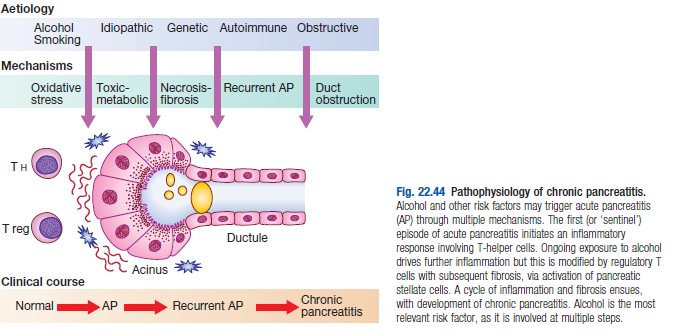
Pathogenesis
- Hyper-secretion and stimulation of exocrine pancreas, plugging of pancreatic duct with protein precipitates
- Causes hypertension in ductal systems
Clinical features
- Pt has history of alcohol abuse. MC in 40s
- 50% of pts have episodes of acute pancreatitis, with each attack resulting in a degree of permanent pancreatic damage
- Abdominal pain – epigastric. Radiation to back
- Some pts have unremitting pain
- Or recurrent episodes that resolves between attacks
- Relived by leaning forwards or by drinking alcohol
- Clinical tetrad – Abdominal pain, anorexia, insulin dependent diabetes, Steathorrea
- First attack at head of pancreas
- Second attack at body and tail – where the beta cells are
- Peripheral neuropathy – related to DM and alcohol
Investigations
- XR – pancreatic calcifications
- CT – golden standard. Pancreatic calcifications , dilated major panc duct, pseudocyst formation
- Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography ERCP – protein ppt, ductal dilation
- Pancreatic function test – Lundh’s test
- Meal of protein, carbs, fats injected into stomach
- Sample of duodenal juice taken & activity of trypsin measured
- Positive test – low trypsin activity means decreased exocrine function of the pancreas
Treatment
- Alcohol avoidance
- Pain relief – NSAIDs, opiates (pethidine [75mg])
- Oral pancreatic enzyme supplements – suppress panc secretion, can reduce analgesic consumption in pts
- Dietary fat restriction (need fat soluble vitamins – ADEK)
- Lansoprazole [30mg b.i.d] to optimise duodenal pH for pancreatic enzyme activity
- Celiac plexus neurolysis
- Surgery
Complication
Aneurysm, splenic vein thrombosis, carcinoma
