2 types of crystals Na urate and Ca pyrophosphate . Differ in shape and properties in polarised light exposure.
Etiology/Epidemiology
- Purine rich foods, high saturated fats, alcohol, fructose
- 10x males, obesity, hyperlipidemia, DM, ischaemic heart disease
- Genetic defect xanthine oxidase (hypoxanthine > xanthine > uric acid)
- Hyperuricemia (male 420μmol/L + 2SD, Female 360μmol/L +2SD)
Pathology
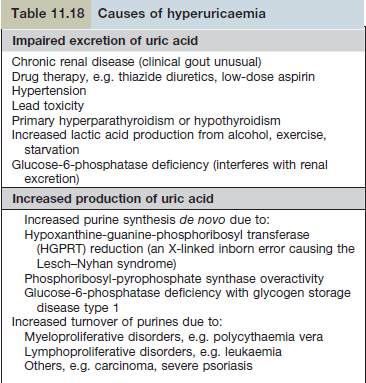
- Elimination of uric acid 2/3 kidneys, 1/3 intestines
- 90% pts have impaired excretion and 10% have increased production (high cell turnover), 1% have in born errors metabolisms.
- URAT-1 and GLUT-9 transporters > uric acid back into circulation. Blocked by probenecid.
- Ingestion of Na urate via neutrophils cause cytokine release IL-1B/IL-8.
- Insulin resistance increases uric acid reabsorption.
Clinical features
- Hyperuricemia may be asymptomatic, synovitis, fever, malaise, confusion
- Acute gout
- Acute phase > asym period > acute phase (usually within 2y)
- First MTP , may precipitated by dehydration, diuretics, alcohol
- Chronic interval gout
- Acute attacks superimposed w/ low grade inflam (may cause joint damage)
- Chronic polyarticular gout
- In elderly on diuretics or premature allopurinol tx in acute episodes
- Tophaceous gout
- High levels of uric acid, white deposits in skin and joints.
- Ear, fingers, Achilles tendon
- Periarticular desposits seen as punched out bone cysts on XR
- Associated w/ renal impairment/ diuretics
- Urate renal stone
Diagnosis
- Usually clinically
- Joint fluid microscopy
- Serum uric acid (>600) however levels fall immediately after acute attack
DDx
- Septic arthritis, infective cellulitis, reactive arthritis
Treatment
- NSAID
- Naproxen – [750mg immediate then 500 every 12h]
- Diclofenac – [100mg immediately then 50 every 8h]
- Indomethacin – [75mg immediately then 50mg every 8h]
- If renal impairment
- Colchicine [1000μg] or prednisolone
- Reducing uric acid levels (to 360)
- Allopurinol [300-600mg] – never started w/in 1 month of acute attack
- Febuxostat [80-120mg] – non purine analogue, well tolerated and safe in renal impairment