Etiology
- Cirrhosis is present >75% of pts with HCC
- Can be due to HBV (MCC), HCV, haemochromatosis, alcohol, NASH, α1-AT deficiency, anabolic steroids
- Chronic HBV infection is a major RF
- Higher risk in HBeAg-positive patients
- Activated immune cells release reactive oxygen species– cause DNA damage. Creates a cycle of damage and repair
- Can lead to mistakes during repair – leads to carcinogenesis
- Aflatoxin (product of fungus aspergillus)
Pathology
- Macroscopically
- In absence of cirrhosis – tumour appears as a single mass
- Presence of cirrhosis – appears as a single nodule or multiple nodules
- Supplied by the hepatic artery
- Spreads by invasion into the portal vein
- Lymph node mets are common
- Well-diff tumours can resemble hepatocytes – difficult to distinguish from normal liver cytology
Clinical features
- Patients with underlying cirrhosis
- Deterioration in liver function
 Worsening ascites/jaundice/variceal haemorrhage
Worsening ascites/jaundice/variceal haemorrhage
- Other common sx
- Weight loss, anorexia, abdominal pain
- Hepatomegaly
- R.hypochondrial mass
- Abdominal bruit – due to tumour vascularity
- Hepatic rupture with intra-abdominal bleeding
- Screening pts at risk of HCC
- Detected earlier, with increased treatment options
Investigations
- Serum markers
- ↑AFP – >400ng/ml (N=<10ng/ml)
- Imaging
- USS – can detect focal liver lesions. Image enhanced by use of US contrast
- Contrast CT – shows hypervascular appearance of HCC
- Liver biopsy – histology confirmation advised in pts with large tumours who don’t have cirrhosis or HBV
- Screening high risk pts – cirrhosis due to HBV, HCV; haemochromatosis, alcohol, NASH, AAT def
Management
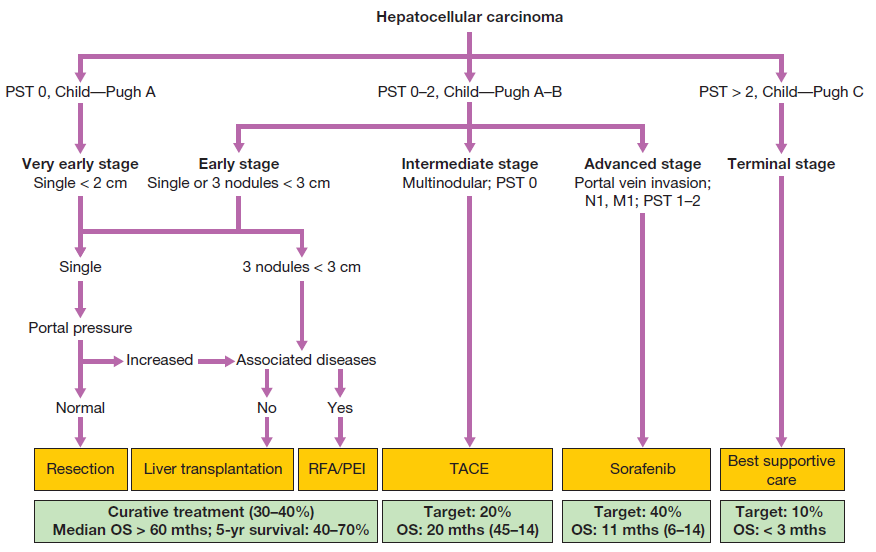
- Cirrhotic patients – see flowchart. Use CLIP score to assess prognosis.
- Prognosis depends on tumour size, vascular invasion and LFTs
- Hepatic resection – treatment of choice for non-cirrhotic patients
- Liver transplantation
- Percutaneous therapy – ethanol injection into tumour under USS guidance
- Radiofrequency ablation (electrode inserted into tumour)
- Trans-arterial chemo-embolisation – hepatic artery embolisation with Gelfoam and doxorubicin
- In cirrhotic pts with unresectable HCC and good liver function
- Chemotherapy
- Sorafenib – multikinase inhibitor with activity against Raf, VEGF + PDGF