- Chronic, progressive cholestatic liver disease. Earlier stage of primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Strongly associated with anti-mitochondrial antibodies (diagnostic)
- Granulomatous inflam of the portal tracts – causes progressive damage and loss of the small bile ducts
- Leads to fibrosis and cirrhosis of liver
Epidemiology
- F:M = 9:1
- MC in cigarette smokers
Pathophysiology
- Closely related with other autoimmune non-hepatic diseases – e.g. thyroid disease
- Genetic association with HLA-DR8
- AMA are directed at pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
- A mitochondrial complex that plays a role in cellular energy generation
- PBC-specific ANA is directed at the nuclear pore antigen gp210 – characteristic staining in IFA (nuclear dots)
- Shouldn’t be mistaken for homogenously staining ANA in autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)
- Elevation in serum Igs – typically IgM (unlike AIH)
- Chronic granulomatous inflammation destroys the interlobular bile ducts
- Progressive lymphocyte-mediated inflam damage causes fibrosis
- Spreads from the portal tracts to liver parenchyma, eventually leads to cirrhosis
Clinical features
- Systemic sx such as fatigue may precede a diagnosis for years. Pruritis (common)
- Bone pain/fractures – due to osteomalacia (fat-soluble vitamin malabsorption) or osteoporosis (hepatic osteodystrophy)
- Weight loss
- Jaundice prominent in late disease
- Xanthomatous deposits around eye
- Mild hepatomegaly (common)
- Splenomegaly – increases as portal HTN develops
- Associated diseases – Sicca syndrome , systemic sclerosis, celiac disease, thyroid disease
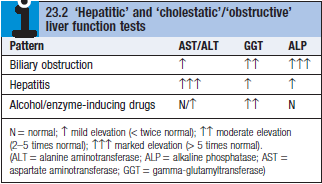
Investigations
- LFTs – ↑ALP
- ↑cholesterol
- AMA – 95% pts
- ANA + ASMA – 15% pts
- USS – alteration of liver architecture
- MRCP/ERCP
- Liver biopsy – portal tract infiltrates, fibrosis
Management
- Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) [13-15mg/kg/d]
- Improves bile flow, replaces toxic bile acids, reduces apoptosis of biliary epithelium
- Immunosuppressants – corticosteroids, azathioprine, penicillamine, ciclosporin
- Pruritis – main sx requiring treatment
- Colestyramine (anion-binding resin) – [4-16g/d PO] mixed in orange juice
- Rifampicin – [150mg/d]
- Naltrexone (opioid antagonist) – [25mg/d]
- Transplant (bilirubin >5.8 mg/dl)
- Malabsorption – replacement of fat soluble vitamins (ADEK)
- Bone disease – calcium and vit D3. Bisphosphonaes if osteoporosis
DDx
Sarcoidosis, brucellosis, parasites, TB
