Rheumatism. Rheumocarditis
1. ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER
Etiology
- MC in children – 5-15 year olds
- Endemic in Asia, Africa, S.America
- Triggered by an immune-mediated delayed response to infection with group A strep
Pathogenesis
- Group A strep have antigens that can cross react with cardiac myosin and sarcolemma membrane protein
- Antibodies are produced against the strep antigens
- Cause inflam in the endo, myo and pericardium
- And in joints and skin
- Histology
- Achoff nodules in the heart – pathognomic feature
- Composed of multinucleated giant cells surrounded by macrophages and T cells
- Fibrinoid degeneration in the collagen of connective tissue
- Achoff nodules in the heart – pathognomic feature
Clinical features
- Fever, anorexia, lethargy, arthralgia – 2 weeks after episode of streptococcal pharyngitis
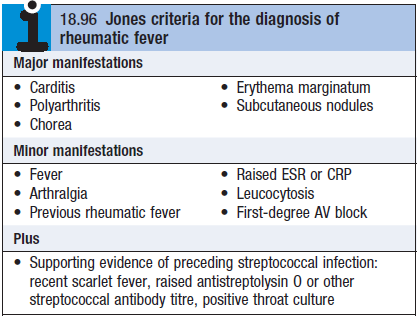 Dx made by Jones critera
Dx made by Jones critera
- 2 or more major manifestations, or
- 1 major and 2 minor, and
- Evidence of preceding strep infx
Carditis
- Pancarditis
- Can manifest as breathlessness, palpitations, CP
- Tachycardia, cardiac enlargement
- Carey Coombs murmur – soft mid diastolic murmur
- Due to valvulitis with nodules forming on the MV leaflets
- Pericardial friction rub
Arthritis
- Occurs early when ASO titres are high
- Acute painful, asymmetric, migratory inflam of the large joints (knees, ankles, elbows, wrists)
- Joints are red, swollen, tender
- Pain responds to aspirin
 Skin lesions
Skin lesions
- Erythema marginatum – red macules that fade in the centre
- On trunk and proximal extremities, NOT on face
- Subcutaneous nodules – small, firm, painless on extensor surfaces
Sydenham’s chorea
- Late neurological manifestation – >3 months after episode of ARF
- Emotional liability – first feature
- Involuntary movements of hand, feet, face
- Explosive speech
Diagnosis – see box
Treatment
- Benzyl pen/oral phenoxymethylpen to eliminate residual strep infx (use clarithromycin if allergy)
- Bed rest and supportive treatment
- Aspirin – pain relief confirms diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever
- Corticosteroids
- Long term prophylaxis against further strep infx – benzathine pen (sulfadiazine/erythromycin if pt is allergic to pen
2. CHRONIC RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE
- Develops in 50% of pts with ARF with carditis
- MC in women
- Mitral valve is affected in 90% of cases
Pathology
- Progressive fibrosis of heart valves
- Fusion of MV commissures and shortening of the chordae tendineae – leads to mitral stenosis
- After valve is damaged, altered hemodynamic stress further increases the damage
