- Cardiac arrest – sudden and complete loss of CO due to asystole, ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation, or loss of cardiac contraction (pulseless electrical activity)
- Clinical dx is based on pt being unconscious and pulseless
Sudden cardiac death
- See box
- Due to massive arrhythmia – VF, pulseless ventricular tachycardia, asystole, or pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
- Coronary arterial disease (CAD) is the most common condition leading to cardiac arrest – VF/VT is common in first few hours of MI

Cardiac arrest
VF and Pulseless VT
- VF – rapid, ineffective, uncoordinated movements of the ventricles
- Therefore produces no pulse
- ECG – rapid, bizarre, irregular ventricular complexes
- VT – can cause cardiac arrest if the ventricular rate is so rapid that effective mechanical contraction and relaxation cant occur
- Can degenerate into VF
- Defibrillation can restore CO but chances of survival decrease by 10% each minute
Asystole
- Occurs when there is no electrical activity within the ventricles
- Due to failure of conducting tissue or massive ventricular damage
- A precordial thump, external cardiac massage or IV atropine/adrenaline can restore cardiac activity
- Permanent pacemaker implantation is required in conduction failure if pt survives
Pulseless electrical activity
- Occurs when there is no effective CO despite the presence of organised electrical activity
- Reversible causes – hypovolaemia,
- Cardiac tamponade, Tension pneumothorax
- But more often due to catastrophic causes – cardiac rupture or massive PE
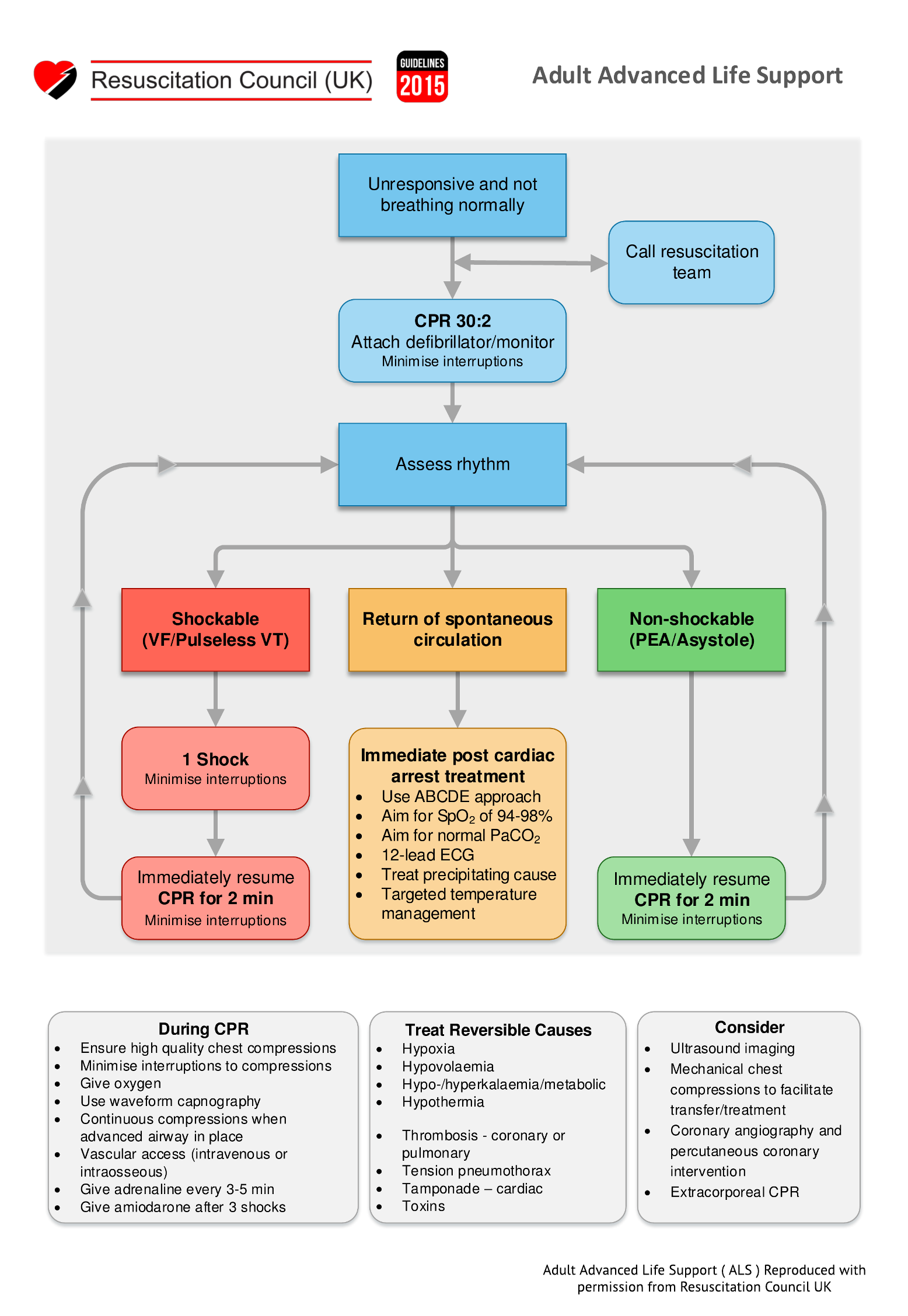
Management of cardiac arrest
Basic life support
- Aim to maintain low level of circulation until ALS can be given
- ABCDE approach
- Airway – assessment and restoration
- Breathing – maintain ventilation by ‘mouth to mouth’
- Circulation – chest compressions
- Disability – assess Neurological status
- Exposure – remove clothes to enable defibrillation; assess for rashes (anaphylaxis)
Advanced life support
- Restore normal cardiac rhythm by defibrillation – if cardiac arrest is due to arrhythmia
- Restore CO by correcting other reversible causes of cardiac arrest – 4 Hs + 4 Ts (see algorithm)
- Intubation to restore ventilation
- During resuscitation, adrenaline [1mg IV] should be given every 3-5 mins. Amiodarone [300mg] after 3rd shock.