- Syncope – transient loss of consciousness due to reduced cerebral blood flow
Vascular
Vasovagal attack
- Simple faint – MCC of syncope
- Due to prolonged standing, excessive heat, large meal
- Mediated by Bezold-Jarisch reflex
- A combo of sympathetic nervous system (SNS) activation and ↓venous return due to an impaired vasoconstrictor response to standing leads to vigorous contraction of under-filled ventricles
- This stimulates mechanoreceptors in LV wall – produces parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) activation and SNS withdrawal
- Causes bradycardia and/or vasodilation
- These trigger reflexes via CNS which reduce ventricular stretch – causes further vasodilation and drop in blood pressure.
- Episodes are associated with prodrome of dizziness, nausea, swearing, sinking feeling
- Pt feels better after lying down
- Postural hypotension
- Drop in SBP ≥20mmHg on standing up from a sitting/lying down position
- Usually, reflex vasoconstriction prevents a drop in BP
- But if this is absent or patient is fluid-depleted, on vasodilating or diuretic drugs then hypotension occurs
Carotid sinus syncope (hypersensitive carotid sinus syn)
- In HCSS, the baroreceptor is sensitive to external pressure – e.g. wearing a tight collar
- Pressure over the carotid artery causes an inappropriate vagal discharge – leads to reflex bradycardia and vasodilation
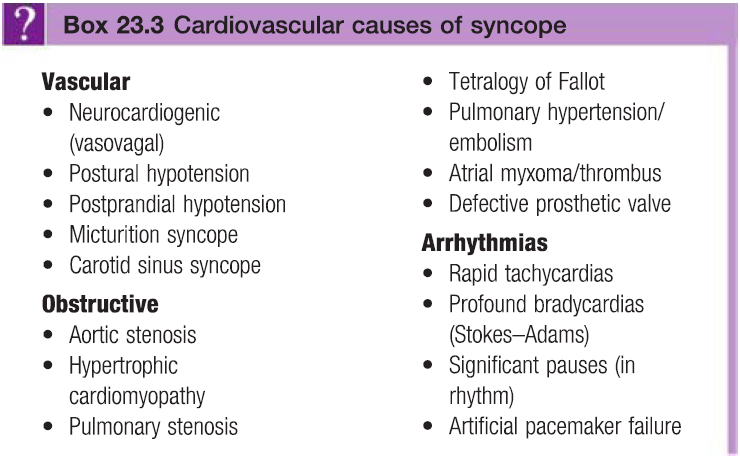
Obstructive – see box
- Lead to syncope due to restriction of blood flow from the heart into the rest of the circulation
- Stokes-Adams attack – sudden loss of consciousness due to intermittent AV block or bradycardia
- Pt suddenly falls to the ground, is pale and deeply unconscious