Etiology
- Most commonly due to rheumatic heart disease – Group A β-hemolytic strep
- Rare – congenital; calcification/fibrosis in the elderly
- Lutembacher’s syndrome – atrial septal defect + mitral valve stenosis
Pathophysiology
- Normal MV orifice 5cm2. Can be reduced to 1cm2 in severe MVS (symptoms occur at <2cm2)
- In rheumatic MVS the mitral valve orifice is slowly diminished due to
- Progressive fibrosis
- Calcification of the leaflets
- Fusion of the cusps and subvalvular apparatus
- Flow from LA to LV is restricted
- LAP rises – leads to pulmonary venous congestion and SOB
- Dilation and hypertrophy of LA
- Filling of LV becomes more dependent on LA contraction
- Any increase in HR shortens diastole when the MV is open
- Produces a further rise in LAP (as more blood remains in LA)
- Progressive dilation of LA can cause AF
- AF + tachycardia → rapid rise in LAP → can lead to pulmonary oedema + HF
- In contrast, slow rise in LAP leads to ↑PVR, which leads to Pulmonary HTN (PHTN)
- Which can protect the pt from pulmonary oedema
- PHTN leads to RV hypertrophy and dilation, tricuspid regurgitation and right heart failure
Clinical features
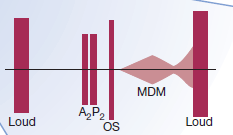
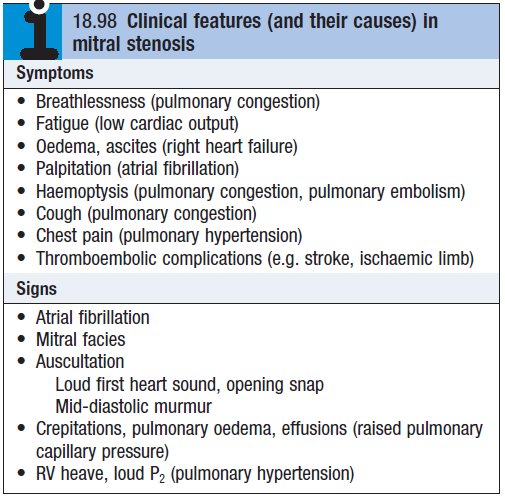 Loud S1 – because forces that open and close the MV are increased as LAP increases
Loud S1 – because forces that open and close the MV are increased as LAP increases
- However S1 can be inaudible if valve is heavily calcified
- Opening snap (normally MV opens silently)
- Mid diastolic murmur – due to turbulent flow
Diagnosis
ECG
- LA hypertrophy – AF, bifid P waves
- RVH – RAD, tall R waves in V1
CXR
- Enlarged LA (characteristic doming)
- Calcified MV
- Signs of pulmonary oedema
Echo (diagnostic)
- Thickened immobile cusps
 Enlarged LA
Enlarged LA- Reduced rate of diastolic filling of LV
Doppler
- Turbulent flow across MV
Management
 Medical
Medical
- Anticoagulation – reduces risk of embolism
- Digoxin, beta blockers, CCB – ventricular rate control for AF
- Diuretics – for pulm congestion
- Mitral balloon valvuloplasy and valve replacement
- Valvuloplasty if criteria is filled (see box)
- Follow up pts yearly to assess for re-stenosis
- Valve replacement – if valve is rigid and calcified
